Flexible Perovskite Solar Cell Market: Trends & Forecast To 2032
The flexible perovskite solar cell market is rapidly transitioning from laboratory research to practical product applications. Projections indicate substantial growth, with the market size expected to surge from $59.92 million in 2024 to $94.20 million in 2025, and further escalating to $815.58 million by 2032. This impressive expansion reflects a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 30.97%, as highlighted in a forecast by Fortune Business Insights. This remarkable growth is fueled by the unique advantages of flexible perovskite cells, such as their lightweight, thin, and printable nature. These characteristics make them ideal for applications where traditional silicon cells fall short, including curved facades, wearable electronics, transportation exteriors, and Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) manufactured using roll-to-roll processes.
Currently, the Asia-Pacific region dominates the market, holding approximately 39.8% of the market share in 2024. This underscores the region's leading role in the global commercialization efforts of flexible perovskite solar cell technology. The ongoing global competition to bring these innovative solar cells to market is intensifying, promising further advancements and broader applications in the coming years. The continuous development and deployment of flexible perovskite solar cells are expected to significantly impact the renewable energy sector, offering versatile solutions for various energy needs.
Why Flexible Perovskite Cells are Crucial Now
Perovskite materials offer a compelling combination of high experimental efficiency and low-cost, solution-based manufacturing. This makes them an attractive alternative to traditional solar cell materials. When integrated with flexible substrates and roll-to-roll manufacturing techniques, perovskite solar cells enable the creation of photovoltaic devices with several key advantages. These advantages are pivotal in driving the adoption of this technology across various industries.
- Ultra-lightweight and flexible: These cells can adhere to curved and moving surfaces, expanding their applicability in diverse environments. The flexibility and lightweight nature of perovskite cells allow them to be used in scenarios where rigid solar panels are impractical.
- Tunable transparency: The ability to adjust the transparency of perovskite cells makes them ideal for windows and facades, seamlessly integrating solar energy generation into building design. This feature enhances the aesthetic appeal of buildings while contributing to energy efficiency.
- Cost-effective mass production: Compared to crystalline silicon, large-scale printing of perovskite cells is significantly more affordable, reducing the overall cost of solar energy generation. This cost advantage is a critical factor in the widespread adoption of perovskite technology.
These unique properties position flexible perovskite cells as a game-changing technology for creating energy-harvesting surfaces that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also portable and seamlessly integrated. The potential for these cells to be incorporated into everyday objects and surfaces marks a significant step forward in the evolution of solar technology. Their versatility and cost-effectiveness make them a compelling solution for a wide range of energy needs, from powering small electronic devices to contributing to the energy supply of entire buildings.
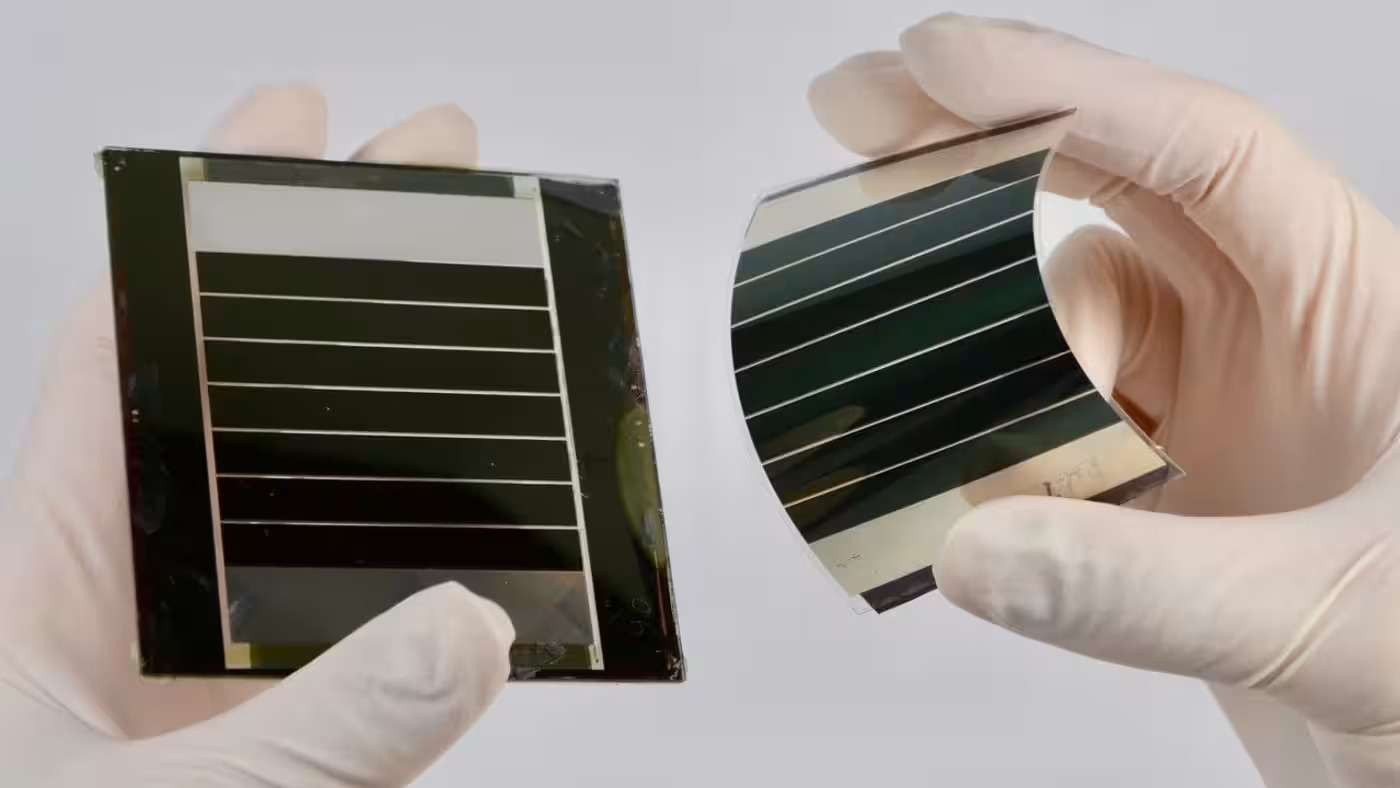
Already a Game Changer
Flexible perovskite technology is transitioning beyond the demonstration phase and entering niche commercial applications where rigid panels cannot compete. This shift underscores the growing maturity and viability of flexible perovskite cells as a practical energy solution. Their unique characteristics open up new possibilities for solar energy integration in various sectors.
- BIPV and Facade Films: These are semi-transparent, thin films designed for windows and exterior surfaces, allowing buildings to generate their own power while maintaining aesthetic appeal. The integration of solar technology into building design represents a significant step towards sustainable construction practices.
- Consumer Electronics and IoT: Flexible perovskite cells are ideal for self-powered sensors, e-paper, and smart tags, exemplified by Saule's inkjet modules. This application highlights the potential for perovskite cells to power a wide range of small electronic devices, reducing the need for traditional batteries and promoting energy efficiency.
- Transportation and Mobility: Lightweight modules for boats, EV roofs, and trailers are crucial in this sector, where minimizing weight is paramount. The integration of flexible solar cells in transportation applications can significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions, contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
- Portable Power: Foldable chargers and rollable modules are well-suited for remote and off-grid use, providing reliable power sources in areas where traditional electricity grids are unavailable. This application underscores the potential for flexible perovskite cells to address energy needs in remote and underserved communities.
Source: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/jp/柔軟なペロブスカイト太陽電池市場-113655
Major Market Drivers and Friction Points
Understanding the factors that drive and hinder the growth of the flexible perovskite market is crucial for stakeholders. These insights inform strategic decisions and guide future developments in the field.
Drivers
- Form Factor Freedom: The flexibility, curvature, and transparency of perovskite cells enable PV integration on diverse surfaces, expanding their application potential. This adaptability is a significant advantage over traditional solar panels.
- Manufacturing Economics: Solution processes and potential roll-to-roll scaling promise significantly lower capital expenditure per unit area, making perovskite cell production more cost-effective. This economic advantage is key to driving market growth and adoption.
- Application Pull: BIPV, wearables, and transportation applications create deployment pathways that do not directly compete with rooftop silicon, opening up new market opportunities. These niche applications provide a strong foundation for the broader adoption of perovskite technology.
- Rapid Efficiency Improvements: Ongoing lab advancements, including records in indoor and tandem devices, enhance commercial attractiveness. Continuous improvements in efficiency are critical for perovskite cells to compete with established solar technologies.
Friction Points
- Stability and Durability: Perovskites are sensitive to moisture, heat, and UV light, making encapsulation and long-term reliability major challenges. Addressing these stability issues is crucial for the widespread adoption of perovskite solar cells.
- Mechanical Robustness: Flexible modules must withstand cracking, peeling, and repeated bending, requiring robust materials and designs. Ensuring mechanical durability is essential for the longevity and performance of flexible perovskite cells.
- Scale-Up Complexity: Translating small-area performance to large, uniform, defect-free rolls is not straightforward. Overcoming these scale-up challenges is critical for the mass production and commercial viability of perovskite cells.
- Supply Chain and Standards: Certification, safety, and recycling pathways for perovskite films are still being established. Developing clear standards and supply chains is necessary to build confidence in the technology and facilitate its integration into the market.
Who's Buying What – Product and Methodology Trends
The demand for perovskite products is shaped by use cases and processing routes, influencing the direction of market growth and development.
Play Structure
- Planar cells are currently the mainstream in flexible forms due to their ease of layer-by-layer fabrication on polymer films. This architecture simplifies the manufacturing process and enhances the scalability of perovskite cell production.
- Mesoporous designs remain relevant for several stability and interface engineering approaches, indicating their continued importance in certain applications. These designs offer unique advantages in terms of stability and efficiency, making them a valuable option for specific use cases.
Method
- Vapor deposition methods are gaining traction for achieving uniform, low-defect films, making them attractive for companies targeting commercialization. This technique ensures high-quality films, which are essential for the performance and longevity of perovskite cells.
- Solution (printing/coating) routes (spin coating, slot-die, inkjet) ensure the lowest cost and best compatibility with roll-to-roll lines. These methods offer significant cost advantages and are well-suited for large-scale manufacturing, making them a key focus for commercial production.
End User
- BIPV is the single largest initial market (windows, facades, shading elements), driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient buildings. The integration of perovskite cells into building materials represents a significant market opportunity.
- Power plants and large-scale PV will likely remain silicon-dominated until perovskite scales and stability are proven. Silicon remains the dominant material in these applications due to its established reliability and scalability, but perovskite cells have the potential to gain ground as their technology matures.
- Transportation, mobility, and consumer electronics are high-value niches where weight and form factor are prioritized over pure efficiency. These applications leverage the unique advantages of flexible perovskite cells, such as their lightweight and adaptability, making them ideal for specialized uses.
Regional Snapshot
The global flexible perovskite market is characterized by regional variations in adoption, research, and manufacturing capabilities. Understanding these regional dynamics is crucial for stakeholders.
- Asia Pacific (Lead): Holds the largest share in 2024, driven by strong manufacturing capabilities and rapid adoption in China, Japan, India, and South Korea. The region's dominance is expected to continue as it invests heavily in perovskite technology.
- North America: Features strong R&D partnerships and early pilots, poised to set manufacturing standards as scale becomes feasible. North America's focus on research and development positions it as a key player in the future of perovskite technology.
- Europe: Benefits from a strong R&D base and pilot deployments (outdoor durability testing, BIPV pilots). Europe's robust research infrastructure and pilot projects are driving advancements in perovskite cell technology and its applications.
- Latin America and Middle East & Africa: Exhibit abundant solar resources and targeted pilot projects, with interest in low-cost, flexible PV for off-grid and building integration. These regions offer significant potential for the deployment of perovskite cells in remote and underserved areas.
Competition and Notable Moves
The competitive landscape of the flexible perovskite market is shaped by both deep-tech startups and thin-film PV specialists. Key players include Saule Technologies, Fab Solar, ART-PV India, Mellow Energy, Swift Solar, Ascent Solar, and numerous Chinese module makers. Recent industry trends, such as pilot projects, outdoor testing, and new module announcements, indicate the market is shifting from lab records to field trials. This is a crucial phase for building confidence in durability and scalability, paving the way for broader commercial adoption.
Where R&D is Placing Big Bets
R&D efforts in the flexible perovskite field are primarily focused on three interconnected areas, each crucial for advancing the technology's commercial viability.
- Stability Engineering: Developing improved perovskite chemistries, interfacial layers, and robust encapsulation methods to withstand years of outdoor exposure. This is critical for ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of perovskite cells.
- Mechanics and Substrates: Creating new flexible conductors and polymer substrates that endure bending without performance degradation. This focus on mechanical durability is essential for applications requiring flexibility and robustness.
- Manufacturing Scale-Up: Transitioning from lab-scale coatings to roll-to-roll deposition with in-line quality control to reduce defects and improve yield. Parallel efforts are also underway to develop perovskite/silicon tandem stacks on flexible substrates and cells optimized for indoor use in IoT devices. Scaling up manufacturing processes is vital for making perovskite cells cost-competitive and accessible for a wider range of applications.
Conclusion
Flexible perovskite solar cells represent one of the most promising pathways toward ubiquitous, integrated photovoltaics, particularly in applications where weight, transparency, and form factor are critical. The market's projected CAGR of approximately 31% underscores the technology's momentum and strong application pull, particularly in BIPV, wearables, and transportation. However, commercialization hinges on resolving stability, mechanical durability, and scale-up challenges.
The strategy for investors and OEMs is clear: support targeted pilot projects in high-value niches (BIPV, IoT, mobility), invest in encapsulation technologies and roll-to-roll quality control, and collaborate across the value chain to drive certification and standards. By addressing these key areas, the flexible perovskite solar cell market is poised to make a significant impact on the renewable energy landscape.
For further insights into the renewable energy sector, consider visiting International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). This organization provides valuable resources and information on the latest trends and developments in renewable energy technologies.